- Nomad Consulting
- Posts
- The Hidden Force Behind a Fourth Industrial Revolution
The Hidden Force Behind a Fourth Industrial Revolution
Why AI-Driven Optimization Is the Game-Changer You Didn’t See Coming

Table of Contents
Discover how reinforcement learning is quietly reshaping manufacturing, logistics, and beyond
We have witnessed three significant industrial revolutions that transformed economies, societies, and daily life. The first harnessed the power of steam, bringing mechanized production to life. The second introduced mass production and electricity, while the third digitized our world with computers and the internet.
We are on the cusp of another exponential shift: the Fourth Industrial Revolution. What makes this era different, and how is artificial intelligence (AI) driving this transformation?
This Revolution is fundamentally moving beyond automation toward a future where machines can learn, adapt, and innovate in surprising ways.
By incorporating advanced techniques such as Reinforcement Learning (RL), this will enable AI to optimize processes, automate decision-making, and unlock hidden efficiencies across sectors like manufacturing, energy, and logistics. In one example use case, AI-driven optimization at Google’s data centers resulted in a 40% reduction in cooling energy, underscoring how RL can deliver transformative outcomes in real-world applications.
The convergence of traditional control systems with AI is enabling smart factories that adapt in real-time, driving the evolution from automated to truly intelligent operations. This quantum leap will empower machines to innovate, explore, and redefine what's possible for industrial efficiency and productivity.
What is Reinforcement Learning (RL)?
Reinforcement learning (RL) is a branch of machine learning where an agent learns to make decisions by interacting with an environment and receiving feedback in the form of rewards or penalties.
Unlike supervised learning, which relies on labeled data, RL involves the agent exploring and exploiting various strategies to maximize cumulative rewards over time.
In scenarios requiring sequential decision-making, such as robotics, gaming, and real-time control systems, RL is an integral technology for automation and optimization tasks in dynamic environments.

Reinforcement Learning and the Fourth Industrial Revolution
In the Fourth Industrial Revolution (Industry 4.0), reinforcement learning is emerging as a critical technology that drives smart factories, adaptive automation, and intelligent decision-making.
Industry 4.0 integrates digital technologies like IoT, big data analytics, and AI into traditional industrial processes, creating a highly interconnected and automated production environment.
RL’s ability to continuously adapt and optimize complex systems in real-time enhances operational efficiency, reducing waste, and enabling autonomous systems capable of making data-driven decisions without human intervention.
This makes Reinforcement Learning a key enabler of these smart, self-optimizing industrial systems.
The Engine of AI Creativity
Reinforcement Learning enables AI to mimic how humans and animals learn through trial and error. By continuously testing and refining its actions based on feedback, reinforcement learning algorithms can identify optimal solutions in environments characterized by immense complexity.
This is particularly valuable in industrial settings where operations involve numerous variables, dynamic conditions, and intricate systems.
Google’s DeepMind is an artificial intelligence research lab acquired in 2015. DeepMind is best known for its pioneering work in deep learning and reinforcement learning, two advanced fields in AI.
In this use case, reinforcement learning was applied to manage and optimize data centers.
Traditionally, operating these facilities relied on a mix of human intuition, hard-coded rules, and manual adjustments. But reinforcement learning offered a completely new approach.
It mapped out potential strategies and discovered operational efficiencies that human engineers had never identified. The results generated a 40% reduction in energy consumption, achieved purely through software optimization, without any changes to the physical infrastructure.
What’s remarkable is not just the energy savings but the fact that AI was able to teach the engineers who built these systems new ways to improve them.
The AI system made counterintuitive decisions which human operators initially doubted; however, those decisions led to significant performance gains.
This highlights a key aspect of the Fourth Industrial Revolution: AI is not just about doing what we already know, but about unlocking new knowledge and creative solutions from raw data.
Advantages of Using RL in Industrial Applications
Reinforcement learning offers several advantages in industrial applications, primarily due to its capacity for real-time learning and adaptation.
Unlike traditional automation systems that rely on fixed rules, RL agents can continuously improve performance by learning from ongoing operations.
This adaptability is crucial in dynamic environments, where operational conditions frequently change. RL’s ability to explore vast action spaces allows it to discover optimal strategies that human operators or conventional algorithms might overlook.
Additionally, RL’s focus on maximizing cumulative rewards leads to significant improvements in efficiency and cost reduction. For predictive maintenance use cases powered by RL, this can reduce equipment downtime and extend asset life.

Current Case Studies and the Future of Reinforcement Learning
Several case studies underscore the transformative impact of reinforcement learning in industrial applications:
1. Google’s implementation of DeepMind’s RL algorithms in its data centers is a prime example. By optimizing cooling systems, Google achieved a staggering 40% reduction in energy used for cooling, a feat previously unimaginable with traditional control methods.
The system’s ability to continuously learn and adapt in real-time allowed it to identify novel, energy-efficient strategies that even seasoned engineers had overlooked.
2. The AlphaGo project by DeepMind demonstrated RL’s ability to solve highly complex problems and was instrumental in applying similar techniques for industries like manufacturing and logistics.
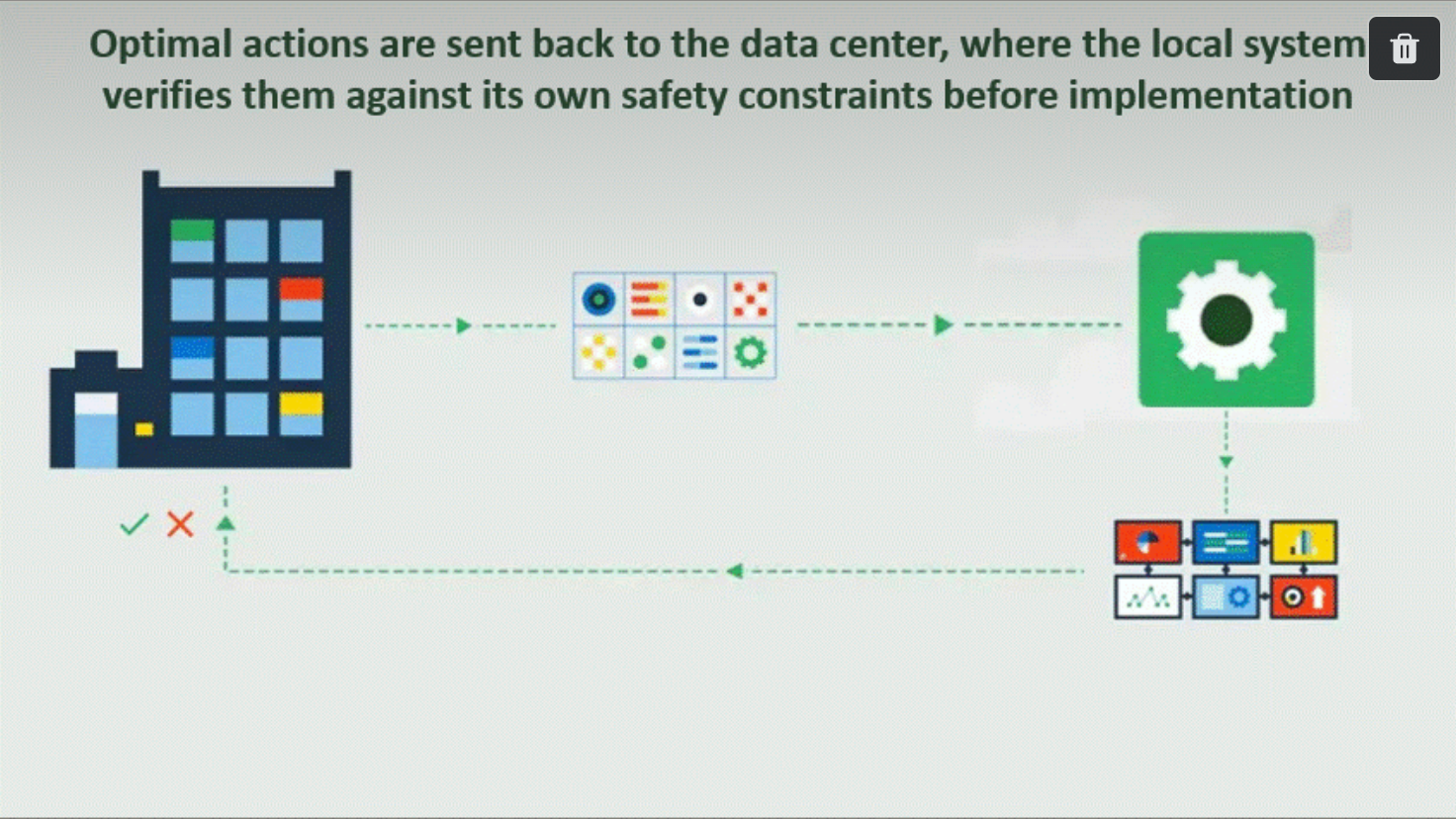
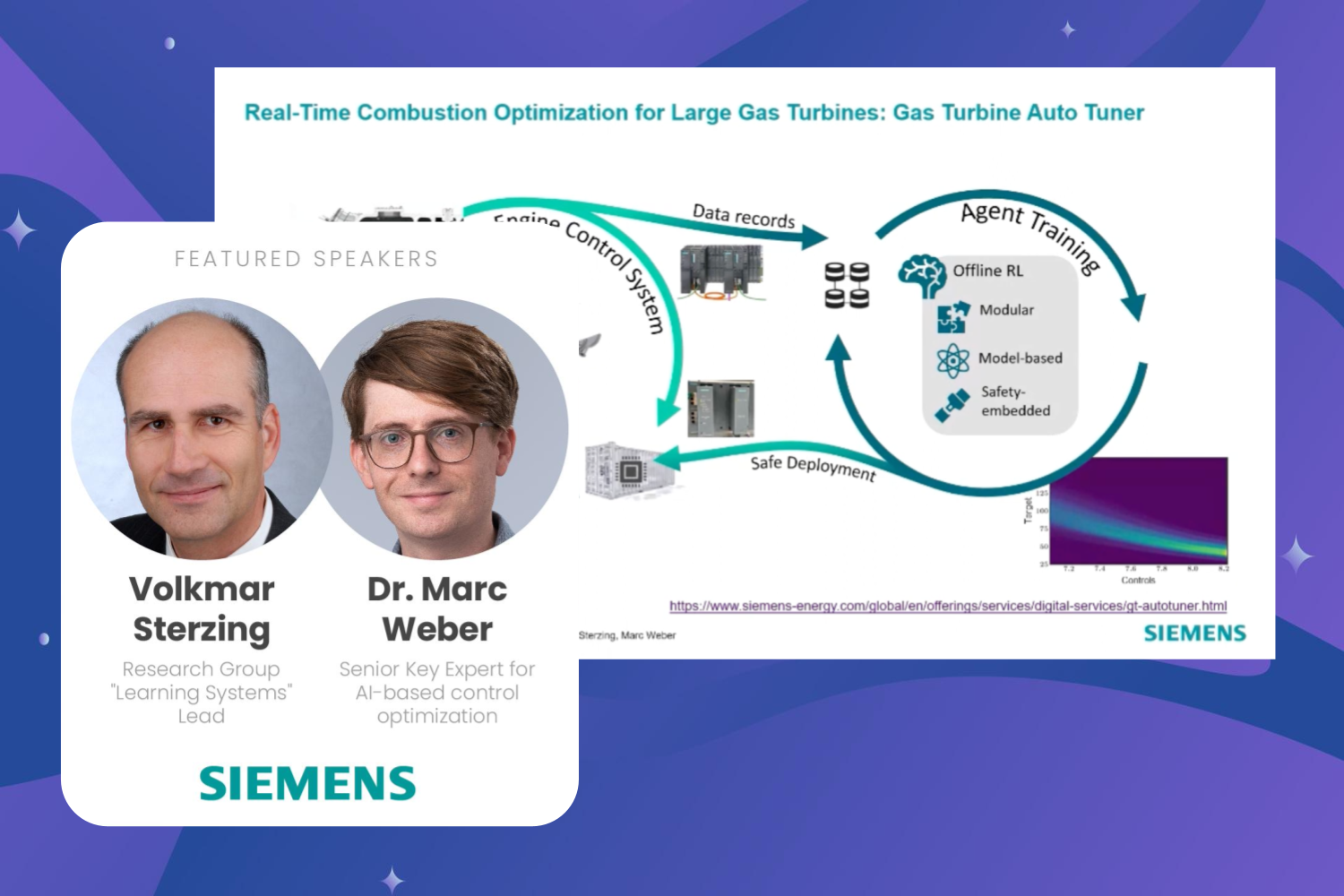
3. Siemens has leveraged RL across various sectors, including energy, transportation, and logistics. Reinforcement Learning was applied to optimize gas turbines and control wind farms.
Siemens has also incorporated RL into its smart factories, where the technology is used to automate decision-making processes and improve overall equipment effectiveness.
The future of reinforcement learning (RL) in Industry 4.0 and beyond represents a critical tool in driving intelligent automation, optimizing complex processes, and enabling autonomous decision-making.
As industries evolve into highly interconnected systems powered by data, reinforcement learning offers the potential to significantly enhance efficiency, adaptability, and innovation.
As businesses successfully integrate RL into their operations, they will be better positioned to thrive in a highly competitive and rapidly changing landscape. Looking ahead, RL’s ability to continually learn and improve will unlock new opportunities, pushing the boundaries of what’s possible in intelligent automation and industrial innovation.